The following reading list for what certainly appears to have been a course on business cycles was found in Joseph Schumpeter’s papers. The original typed copy (it is not a carbon copy) is four pages long and lacks a heading with a course name or number, date, or instructor’s name so we cannot even be 100% confident that it can be associated with any Harvard course. It is simply included in a folder with miscellaneous Schumpeter notes (above my pay-grade to extract any more than a random word or two per page from Schumpeter’s scribble cum shorthand).
One important fact is that the latest item on the reading list is an August 1942 Q.J.E. article by Samuelson. So my theory of the case leads me to assume that this artifact comes from a business cycle course taught at Harvard during the 1942-43 or perhaps 1943-44 academic year. I note that Schumpeter taught the courses “Economic of Socialism”, “History and Literature of Economics since 1776”, and “Advanced Economic Theory” in both those years. Neither of the first two titles is anywhere close to a dedicated course on business cycles. A look at the reading lists and exams for the 1941-42 version of “Advanced Economic Theory” finds that economic dynamics (both micro- and macrodynamics) was one of several topics covered in the second semester, but nothing like the exclusive focus on the theory of business cycle as seen in the reading list below.
Alvin Hansen taught an undergraduate course “Business Cycles” (Economics 45a) and a graduate course “Business Cycles and Economic Forecasting” (Economics 145a), but a reading list with the title “Specific Reading Assignments in Economics 45a” for 1943 and the exams for both Economics 45a and 145a do not give multiplier-accelerator topics as much emphasis as seen in the reading list transcribed in this post.
The only other candidate (assuming that this reading list had been prepared for a Harvard economics course) appears to be the undergraduate course “Introduction to Mathematical Business Cycle Theory” that I believe was taught once and only once at Harvard by Richard M. Goodwin. I find that the “goodness of fit” of the final examination questions to the reading list sufficiently adequate to consider the following reading list and examination questions at least a tentative match for now.
_____________________
Reading list,
tentatively matched to Economics 46,
Mathematical Business Cycle Theory
- Over-All Picture of the Business Cycle.
Schumpeter, J.A., “The analysis of economic change,” R.E.S., XVII (May, 1935), pp. 2-10.
Knight, F.H., “The business cycle, interest, and money: a methodological approach,” R.E.C., XXIII (1941), pp. 53-67.
- Types of Cycles.
Kondratieff, N.D., “The long waves in economic life,” R.E.S., XVII (Nov., 1935), pp. 105-15.
Kitchin, J., “Cycles and trends in economic factors,” R.E.S., V (Jan., 1923), pp. 10-16.
Frickey, Edwin, “The problem of secular trend,” R.E.S., XVI (1934), pp. 199-206.
- Econometric Approach.
Tinbergen, J., “Econometric business cycle research,” R.Ec.Stud., VII (1940), pp. 73-90.
Keynes, J.M., “The statistical testing of business-cycle theories,” E.J., XLIX (Sept., 1939), pp. 558-68; and Tinbergen-Keynes, “On a method of statistical research,” E.J., L (March, 1940), pp. 141-156.
- Saving and Investment.
Lutz, F.A., “Outcome of the saving-investment discussion,” Q.J.E., LII (1937-38).
Lerner, A.P., “Saving and investment: definitions, assumptions, objectives,” Q.J.E., LIII (1938-39), pp. 611-19.
Lange, O., “Saving in process analysis,” ibid., pp. 620-22.
Ohlin, Bertil, “Some notes on the Stockholm theory of saving and investment,” E.J., XLVII (1937), pp. 53-69; 221-40.
- Keynesian Economics.
Hicks, J.R., “Mr. Keynes’s theory of employment,” E.J., XLVI (1936), pp. 238-53.
Lange, O., “The rate of interest and the optimum propensity to consume,” Economica, V (new series, 1938), pp. 12-32.
- Spending Policy and Multiplier.
Kahn, R.F., “The relation of home investment to unemployment,” E.J., XLI (1931), pp. 173-98.
Clark, J.M., “An appraisal of the workability of compensatory devices,” A.E.R., (1939, Suppl.), pp. 194-209.
Williams, J.H., “Deficit spending,” A.E.R., XXX (Feb., 1941, Suppl.), pp. 52-66.
Machlup, F. “Period analysis and multiplier theory,” Q.J.E., LIV (1939-40), pp. 1-27.
Samuelson, P.A., “Fiscal policy and income determination,” Q.J.E., LVI (Aug., 1942), pp. 575-605.
- Acceleration Principle.
Aftalion, A., “The theory of economic cycles based on the capitalistic technique of production,” R.E.S., IX (1927), pp. 165-70.
Clark, J.M., “Business acceleration and the law of demand: a technical factor in economic cycles,” J.P.E., Vol. 25 (March, 1917), pp. 217-35. Reprinted with additional note in Preface to Social Economics.
Tinbergen, J., “Statistical evidence on the acceleration principle,” Economica, V (1938, new series), pp. 164-176.
- Dynamic Models Involving Multiplier and Acceleration Principle.
Samuelson, P.A., “A synthesis of the principle of acceleration and the multiplier,” J.P.E., XLVII (1939), pp. [no pages given]
Kaldor, N., “Model of the trade cycle,” E.J., March, 1940.
- Monetary Theory of the Business Cycle.
Hawtrey, R.G., “The trade cycle,” Dutch Economist and reprinted in Trade and Credit, London, 1928, pp. 82-104.
Hayek, F.A., “Price expectations, monetary disturbances and malinvestments,” first published in German in Nationalökonomisk Tidskrift, Vol. 73, No. 3, 1935. Reprinted in Profits, Interest and Investment, London, 1939, pp. 135-57.
- Overconsumption Theory and Secular Stagnation Thesis.
Robertson, D.H., “A survey of modern monetary controversy,” Manchester School, 1938.
Hansen, A.H., “Progress and declining population,” A.E.R., XXIX (1939), pp. 1-15.
Neisser, Hans, “General overproduction,” J.P.E., XLII (1934), pp. 433-65.
Kaldor, N., “Stability and full employment,” E.J., XLVIII (1938), pp. 642-57.
Ellis, H.S., “Monetary policy and investment,” A.E.R., XXX (1940), pp. [no pages given]
- Harvest Cycles and Other Special Cycles.
Jevons, H.S., “The causes of fluctuations of industrial activity and the price level,” J.R.S.S., XCVI (1933), pp. 545-88. Discussion, ibid., pp. 588-605.
Derksen, J.B.D., “Long cycles in residential building, an explanation,” Econometrica, VIII (1940), p. 10.
Long, C.D., “Long cycles in the building industry,” Q.J.E., LIII (1938-39), pp. 371-403.
Source: Harvard University Archives. Joseph Schumpeter Papers. Lecture Notes Box 2, Folder “Notes”.
______________________
Course Enrollment
[Economics] 46. (spring term) Dr. Goodwin.—Introduction to Mathematical Business Cycle Theory.
Total 4: 3 Navy V-12, 1 Radcliffe.
Source: Harvard University. Report of the President of Harvard College, 1943-44, p. 56.
_____________________
1943-44
HARVARD UNIVERSITY
ECONOMICS 46
Introduction to Mathematical Business Cycle Theory
[Final examination, June 1944]
Part I
Answer both questions.
- Suppose an economic system completely characterized by the multiplier and acceleration principles. Further suppose all data in annual terms and a one year lag in the expenditure of income. If the system shows oscillations with an 8.5 year period, and an amplitude increasing continuously at a .02 rate, what are the values of
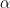 , the marginal propensity to consume, and of
, the marginal propensity to consume, and of  , the acceleration coefficient? Secondly, suppose, being a New Dealer with a difference, you desire to abolish economic cycles. If the values of
, the acceleration coefficient? Secondly, suppose, being a New Dealer with a difference, you desire to abolish economic cycles. If the values of 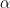 and of
and of  were open to governmental control, state one pair of values for
were open to governmental control, state one pair of values for 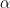 and
and  , at which you might aim and why.
, at which you might aim and why.
- Describe cursorily as many as possible types of ‘dynamization’ useful in business cycle theory and indicate, where you can, your evaluation of their relative importance.
Part II
Answer any two, or three, or four questions.
- Explain the economic meaning of the following terms: endogenous, initial conditions, phase constant (epoch), stationary, static, amplitude, dynamic, and over-damped.
- Discuss thoroughly the role of damping in quantitative cycle theories.
- Do you consider it a correct appraisal of Tinbergen’s statistical work to say: “The method is one neither of discovery nor of criticism”?
- What economic assumptions are involved in the use of second order, homogeneous, linear differential and difference equations with constant coefficients?
- “Is it possible that there could be a cyclical fluctuation in a system, all the ultimate independent determinants of which had fixed regression coefficients and were in linear correlation with their consequences, except in the case where one of the ultimate determinants is itself a periodic function of time (e.g. sun spots)? Where and how does the element of reversal come in?….I should like to know the answer?” How would you answer Lord Keynes? Be concrete.
- Give one example of how inventories may be introduced into cycle analysis and show the more important consequences.
Source: Harvard University Archives. Final Examinations, 1853-2001. Box 9. Papers Printed for Final Examinations: History, History of Religions,…, Economic,…, Military Science, Naval Science. June, 1944.
Image Source: Richard M. Goodwin, in the Harvard Album, 1946.









